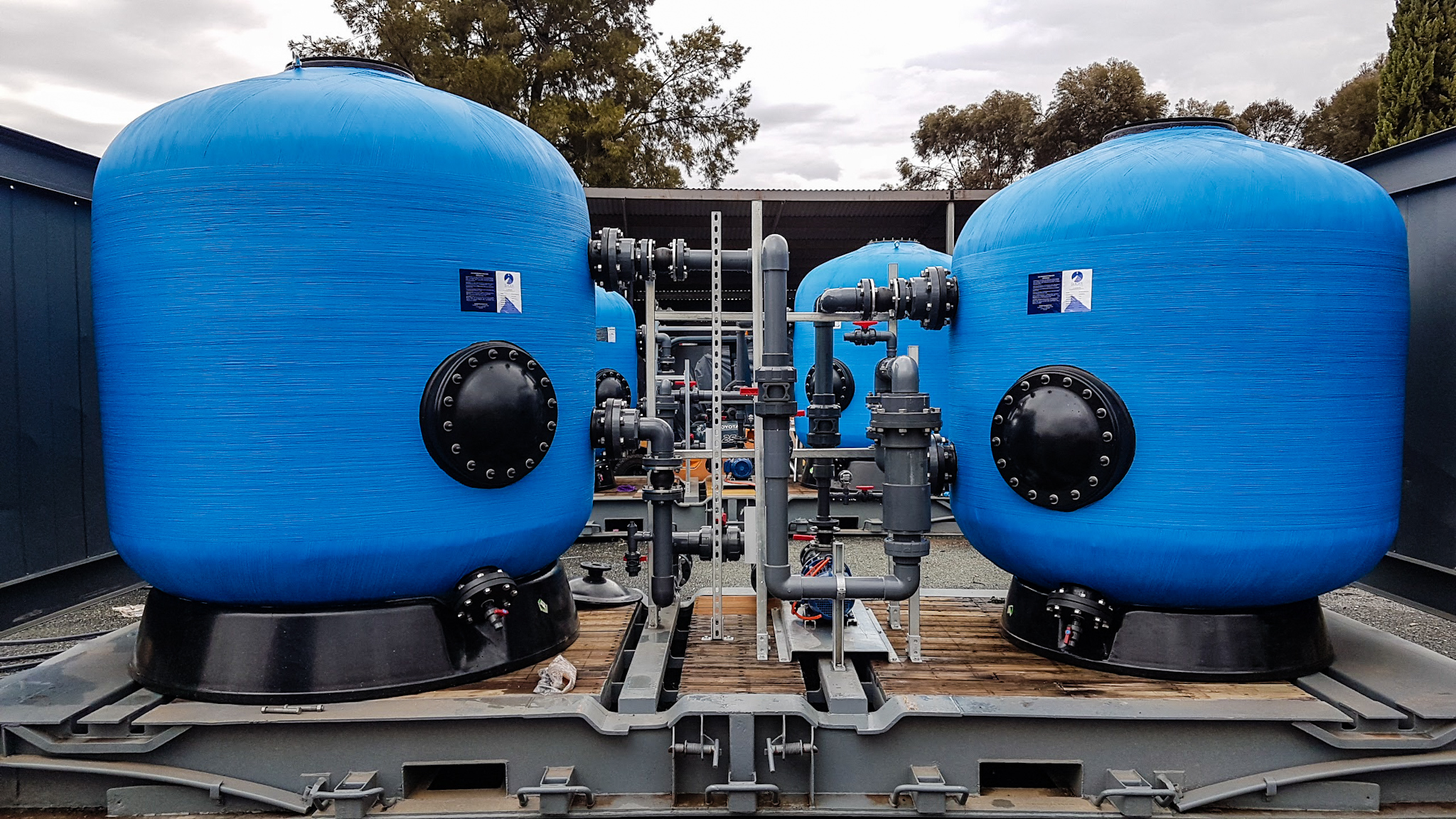
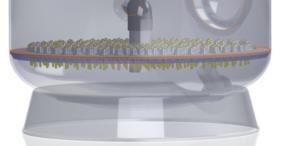
In most applications in a pressure filter, downflow is the most common flow path. Lateral collector arms and nozzle plate floor are options used in the lower section of a pressure filter to perform 3 tasks.
- Collect the filtered water after being treated or filtered from the layer of filter media.
- Backwash the filter media by reversing the flow, creating bed expansion and causing a release of trapped contaminants.
- Slotted openings are sized to ensure there is no media loss during operation.
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between lateral collectors and nozzle plate floors in pressure filters:
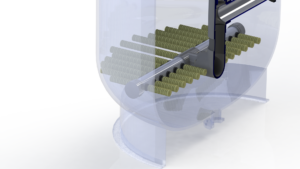
- Lateral Collector Arms in Pressure Filters:
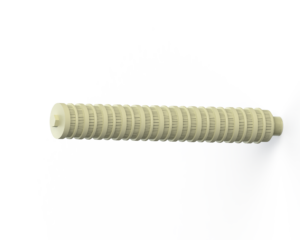
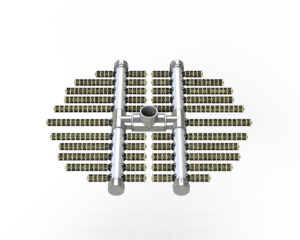
- Lateral collector arms in pressure filters are located at the bottom of the filter vessel beneath the filter media and have a series of slots or holes that collect the filtered water from across the surface area of the filter media, connecting back into a central manifold or hub for the filtered water to exit the vessel.
- Lateral collector arms help maintain an even flow of water throughout the filter bed, ensuring that the entire bed is utilised during the filtration process.
- The primary function of lateral collectors is to prevent channeling, which is the uneven flow of water through the filter media that can lead to incomplete filtration and reduced filter efficiency.
- When backwashing, the lateral collector arms allow even distribution of water across the entire surface area of the filter bed to allow maximum uplift of filter media to release any trapped sediments and contaminants.
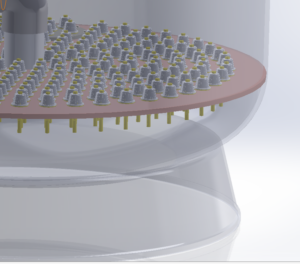
Nozzle Plate Floor in Pressure Filters:
-
- A nozzle plate floor, also known as a distribution or collection plate, is typically found in the lower part of a pressure filter vessel which not only do they collect filtered water from right across the filter surface area, the real benefits of a nozzle plate floor is during backwashing and cleaning the filter media.
- With Nozzle Plate Floor filters, the primary purpose of these is to facilitate air scouring. It is the plate floor and long nozzle tails that allow air scouring to take place, when air is pumped into the bottom dome below the nozzle plate floor the air rises immediately to the underside of the plate floor. It then spreads out to form an ‘air cushion’ under the plate floor(the long nozzle tails are lower than this so at this stage no air can enter the media bed). As the cushion of air increases it eventually enters the nozzle tails simultaneously ensuring even air distribution across the entire filter bed.
- Once the air has filled the entire filter bed, the actual bulk density of the media has been reduced, allowing for a far more effective backwash cycle than if it was performed with water alone.
- During the backwash cycle, the pressurised air/and or water is used to agitate and lift the filter media to remove accumulated solids and debris, essentially cleaning the filter media.
- The nozzle plate floor is essential for the maintenance and periodic cleaning of the filter media to maintain its effectiveness.
To summarise, pressure filters commonly utilise lateral collectors in applications that do not require air scour, such as when using granular activated carbon or calcite. On the other hand, the nozzle plate floor serves a similar purpose as lateral collectors but plays a crucial role in backwashing and cleaning the filter media. Its ability to introduce air into the filter bed ensures optimal performance, making it ideal for heavy sediment and biological filtration applications.